Overview of The United States
Home to half of the world’s top universities, the United States of America (US) is one of the most popular study destinations for international students. Over a million students from around the world study in the US every year, drawn to the high quality of education, highly accredited professors, and the high standard of living.
Location and Geography
The United States of America is the world’s third largest country in size and nearly the third largest in terms of population. Located in North America, the US is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east side and the Pacific Ocean on the west side of the country. It shares its northern border with Canada and its southern border with Mexico. Due to the large size of the US, its geography is extremely diverse including forests, deserts, beaches, mountains, and large bodies of water in and around the country.
States and Territories
The US consists of 50 states, a federal district (Washington, D.C.), five major territories, and various minor islands.
Washington, D.C., formally known as the District of Columbia, is the capital of the United States. Each state and territory also have their own capital cities, listed in Table 1.
More than 10 US cities are listed amongst the top 100 QS Best Student Cities (2019). The top student cities (and the state they are in) in America are: Boston (MA), New York (NY), Los Angeles (CA), San Francisco (CA); Chicago (IL), Atlanta (GA), Philadelphia (PA), Washington (DC), Pittsburg (PA), San Diego (CA), Baltimore (MD), Houston (TX), and Miami (FL).
Climate and Weather
Due to the large size of the US, it has a wide variety of weather conditions across the country at any given time. In general, the US has a continental climate, with cold winters (often frigid) and hot summers (sometimes very hot), with a different season duration depending on a region’s proximity from the equator and from the sea. However, there are some exceptions. The weather on the west coast, bordered by the Pacific Ocean, and in its south most regions, have Mediterranean and tropical climates respectively. The mountainous areas, on the other hand are cold in winter and remain cool in summer, whereas its desserts are mild in winter and extremely hot in the summer. The deserts are mostly found in the southwestern regions of the US.
Languages
English is the primary language spoken in the US. Spanish, Chinese, and Native American are among the top other languages spoken throughout the US.
Religions
Although the US is a predominantly Christian and Catholic country, there are many mosques, temples, and synagogues across the country. The freedom to practice one’s religion is among the most important rights in the United States.
TYPES OF DEGREES

- Associate Degree: It is an academic degree awarded by the community colleges, junior colleges, and business colleges. Usually for two years (60 credits). In USA, an associate degree is equivalent to the first two years of a four-year college or university Bachelor’s degree. It is the lowest in hierarchy of post-secondary academic degrees offered in USA.
- Bachelor’s Degree: Commonly known as Undergraduate degree in India. The duration of the bachelor’s course is 4 years (120-150 credits). Students who have completed a part of their undergraduate degree and want to go to USA, can apply as a transfer student. There are two types of bachelor’s degree: B.A or B.S. Some universities in the USA offer either of the degrees in all fields and at times both the degrees in some field. Students need to appear for SAT & TOEFL/IELTS for admission.
- Master’s Degree: The duration of master’s courses may range from a year or two depending on the university & your area of specialization (30-48 credits). The binding requisite for Masters is 16 year of education. Students with Bachelors in engineering are qualified whereas the students with B. Com, B.Sc., and B.A need to complete at least one year of Masters. Postgraduate diploma is also accepted by some specific institutions for specific programs. Some universities have started accepting 3 years Bachelor’s degree i.e. B. Com, BSc, BA, etc. into their MSc, MA or MBA degree. Exams required are GMAT for management related subjects / GRE for arts, science or any other subjects and TOEFL / IELTS for admission.
- Doctorate: Commonly known as PhD. Duration may range from 3 years to 5 years. Students can take admission for a PhD after completion of their master’s degree. PhD students need to submit a research proposal as well as have to appear for GRE/GMAT & TOEFL/IELTS for admission.
- Summer Program: Are study programs during the months of summer vacation. They usually last from six to ten weeks depending on the school and the course of study. Most summer schools offer a wide variety of courses. Students, who wish to explore courses outside their major, or simply accelerate their degree program, attend Summer Program.
| LIST OF UNIVERSITIES |
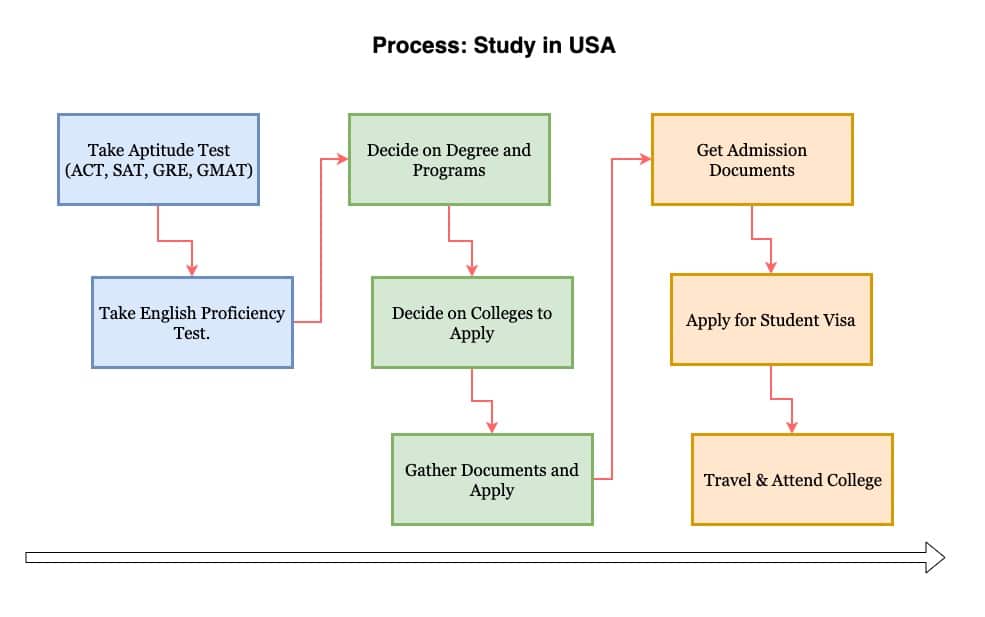
ADMISSION PROCESS
Admission to USA universities and colleges can be very competitive. Each university and department has its own admission requirements of the course of study selected. Successful admission for International students to a top USA school requires ample amount of preparation & research. The admission process should ideally begin at least 6-18 months before your expected arrival in the USA. Organizing and planning are the two vital aspects as timely completion of all the necessary steps is the key.
ELIGIBILITY
- Undergraduate: 10+2
- Graduate:16 years of education required
- Some Institutions accepts 3 yrs of degree i.e. B. Com, BSc, BA, etc. into their Masters or MBA Program.
- Good & strong academic background
- Good scores in entrance exams like SAT, TOEFL, GRE, GMAT, IELTS, etc.
- Strong recommendation letters
- Statement of Purpose/Personal Statement, essays & resume
- Certificates of achievement & extra -curricular activity participation
- Strong financial background.
Application Requirements and Deadlines
Ready to study in the United States? Start by reviewing the admission requirements for each of the programs the student is interested in. To gain admission, students need to satisfy the academic requirements of the course and demonstrate the level of English language proficiency required by the institution.
Exact admission requirements vary from institution to institution and from program to program. Requirements for the same programs can also change over time. Always check the admission requirements before applying.
Academic Requirements
Admission into a study course depends on the student’s past academic performance. Each institution specifies the minimum grades/marks or cumulative averages (GPAs) it will accept. In some cases, students also need to have completed one or more required subjects previously, known as prerequisite subjects.
Language Proficiency Requirements
Since English is the primary language of instruction in the US, students applying from a non-English speaking country need to demonstrate English proficiency through an English language test as part of the admission process. Standardized English language tests evaluate students on their reading, listening, speaking and writing skills.
Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) is the most common language test for universities and colleges in the US. English Language Testing System (IELTS), is also accepted.
Language test score requirements vary by institution and program. Some institutions only look at the overall scores, while others have cut-offs for scores in each of the four skills sections. Typically, students applying to an undergraduate course need one of the below:
- TOEFL (internet-based test, iBT) scores between 60.0 and 100.0 overall
- IELTS scores between 6.0 and 7.5 with no band less than 6.0
Language requirements are stricter for some postgraduate and professional programs. Always refer to the admission requirements for the specific course on the Bright Spark Overseas Education Platform for the most accurate information. Learn more about the English language courses in the Education Pathways for International Students section of this guide.
Application Deadlines 
Colleges in the US offer students one of the following options for applying to an institution:
- Regular Decision (RD): A regular decision is for students who are not 100% sure where they would like to apply. This option allows students to take more time to complete their application or retake their ACT or SATs.
- Early Action (EA): Early action is for students who are unsure about attending a particular school. Students are able to apply to multiple institutions through early action.
- Early Decision (ED): Early decision is for students that know where they would like to go. If a student selects EA, it can be difficult to back out as that can lead to negative consequences as the application is a binding contract.
- Rolling Admission (RA): Rolling admission is an option for students that apply to a school through EA and decided they wanted to attend another one. This option is also available if students finish their application early. Schools can provide students with acceptance quicker through RA.
Each institution is different so it is important to research and learn their policies to ensure students apply right the first time. If students are applying through regular decision, they will submit their application in early January (dates vary per institution). Students will hear back regarding their admission status from March to April. Students applying through early action and early decision have similar deadlines in early November (dates vary per institution). These students will hear back in December. The big difference is that if students are accepted through an ED, they agree to enroll in the institution that accepted them. Rolling admission is more flexible and has a bigger window of time to apply. Applications can be submitted from the fall to the spring of the respected intake year.
Student Visa
 The Government of the United States offers international students three different types of visas depending on the level of schooling they apply for. Before a student can apply for the F, J, or M student visa, they must apply and be accepted by an institution in the US that is certified by the Student Exchange and Visitor Program (SEVP).
The Government of the United States offers international students three different types of visas depending on the level of schooling they apply for. Before a student can apply for the F, J, or M student visa, they must apply and be accepted by an institution in the US that is certified by the Student Exchange and Visitor Program (SEVP).
- F Student Visa: Reserved for students looking to study at a college or university in the US or to study English at an English language institute
- J Exchange Visa: Awarded to students looking to participation in an exchange program at the high school and university level
- M Student Visa: For students looking for non-academic or vocational study or training in the US
Once a student is accepted by a SEVP-certified school, they receive an I-20 or DS-2019 form from the institution’s international student office. These forms are important to present when the student applies for their visa. The Government of the United States has two separate government agencies involved in international student arrival and status while studying abroad.
The two agencies involved are: State Departments (responsible for issuing the visa) and the US Department of Homeland Security (responsible for monitoring student entry to the country).
Students applying for an F1 visa will have strict qualifications to prove which includes:
- Provide proof of intent to return to their home country upon their completion of studies
- Only studying at the institution notes on the visa
- Demonstrating they have sufficient funds to support their life in the US
- Showing they have strong ties to their home country including:
– A job offer for after graduation
– A House, land, etc.
– Bank accounts
– Family
Students are also required to complete a F1 visa interview. This interview determines whether the student is qualified or not. Some examples of F1 visa questions include:
- Why did you choose to study in the US instead of joining the workforce in your home country?
- Why did you choose this school and why is it the best school for you?
- What are your test scores (GRE, GMAT, SAT, TOEFL, IELTS), your GPA, and your overall performance as a student in the past?
- How are you funding the entire duration of your education, including tuition, room and board, transportation, and all other expenses?
After you graduate, will you return home or will you stay in the United States?
If a student is approved, they may be required to pay an insurance fee and have a digital fingerprint scan taken for government records. Students are required to provide their passport to receive the visa. Do not make any travel plans until the student has their visa approved. The visa insurance fee does not guarantee visa approval.
Arriving in the United States
When moving to the US, students must remember to bring the following:
- Passport
- SEVIS Form I-20 or DS-2019
- Evidence of financial resources
- Evidence of student status (such as recent tuition receipts and transcripts)
- Name and contact information for your Designated School Official (DSO), including a 24-hour emergency contact number at your chosen institution
- If the student is an exchange student, they must provide letter from their home university stating their intent to return to their home university
Traveling with a Dependent
International students can be accompanied to the US by their dependent(s) at any time. Dependents are either a spouse or unmarried minor child (under the age of 21). These dependents apply for an F2 or J2 visa at the same time the international student applies or they can at a later date.
Length of Stay
Students have 60 days after completion of their program to leave the US under their F1 visa. If an international student would like to stay in the US, they have two options available to them. Option one is to re-enroll in a post-secondary program. Option two is to apply for a visa status change. Anyone holding an M1 or J1 visa will have a grace period of 30 days after the completion of their course.
Visa Rejections
In the case that a student has their F1 visa application rejected, the reason will be provided to that student. Common reasons applications are denied are as followed:
- Applicant failed to provide the necessary information or support documents
- Fraud or misrepresentation
- Unlawful presence in the United States
- Health-related grounds
- Criminal-related grounds
- Security-related ground
Student Checklist
- Valid passport and Visa: Bring all visa documentation along with a valid passport. Passport must be valid for at least 6 months prior to the entry date in the US. We also recommend keeping multiple copies of the passport and visa documentation.
- Student Enrollment and Orientation Documents: Students should bring their I-20 or DS-2019 forms and the student information pack, which they would have received from the institution.
- Luggage: Pack according to the weather and permitted baggage allowance, and avoid all the restricted items.
- Voltage Converter and Travel Adaptor: Students may need a voltage converter if their appliances do no not work on the same mains voltage as the US (120V 60Hz). A power adapter is needed if appliances have a different plug than the ones used in the US wall socket.
- Flights/Airfare: Book flight in time to arrive for orientation, and keep a record of the flight booking and bring it along to the airport.
- Transportation for the Airport: Obtain ground transportation from the airport to accommodation. Some colleges and universities offer free pickup so be sure to check.
- Accommodations: Plan out the accommodations (secure a place to live), and keep the address, phone number, and lease agreement/payment confirmation with you. Learn more about how to secure your accommodations in the Living in the US section of this guide.
- Contact Details: Create an emergency contact list, as well as your embassy, accommodation and institution details.
- Medication and Toiletries: Learn how to travel with medication and what documentation the student needs to bring with them.
- American Currency: Consider bringing a small amount of cash (~US$500) with you. Monetary instruments, including cash and traveller’s cheques, valuing at or more US$10,000 (or its foreign equivalent) must be declared at customs. Learn more.
What to Bring
Before packing, an incoming student should:
- Verify luggage restrictions with their airline
- Pack for the weather -we recommend researching the weather in the city of stay to pack accordingly
- Check which items the US Customs and Border Protection does not permit through customs (e.g. pets, plants, fresh fruits and vegetables, meat products, etc.)
Carry-On Items
Upon arrival, students will be asked to show their travel documents to the officers in immigration clearance before then can exit the airport. Students must keep these items, and any other related study documentation, in their carry-on luggage. Checked luggage is collected after the student passes the immigration clearance.
We recommend keeping the following items in the carry-on:
- A valid passport
- A valid study visa
- SEVIS Form I-20 or DS-2019 forms
- Confirmation of Enrolment, and any other institution documentation student received
- Original or certified copies of your academic transcripts and qualifications
- Other personal identification documents, e.g. birth certificate, ID card, driver’s licence
- Medical records and/or prescriptions
- Evidence of financial resources
- Name and contact information for your Designated School Official (DSO), including a 24-hour emergency contact number at your chosen institution.
- Important telephone numbers and addresses in home country and in the US
- Details of accommodations, including proof of payment (if payment was made)
Arrival at the Airport
When coming to the US, students are required to do the following things:
- Before landing in the US, complete a Customs Declaration Card—cards are distributed on the airplane prior to landing
- Upon arrival, follow the signs for “Immigration and Customs Clearance”
- Enter the line for non-American passport holders
- When called by Immigration Officer, present them with the passport, visa documents and the Incoming Passenger card
- Have your SEVIS Form I-20 or DS-2019 forms and accommodation details with you as the officer may ask for them
Common Questions Asked at Arrivals
Below is a list of commonly asked questions that students may be asked when they arrive at the airport by Immigration Officers:
- What is your name?
- Where are you from? What is your home address?
- What is your mother’s and father’s name?
- What is your date and place of birth?
- What school are you going to attend in the US?
- What program are you going to study and how long is the program?
- What are your plans after completing the program?
- Who packed your bag(s)?
- Do you know what’s inside the bags?
- How much cash are you carrying with you?
- How are you paying for your education?
- Do you have relatives/friends/family in the US? If yes, where do they live? If no, where will you stay?
- Is someone coming to pick you up at the airport?
Students should respond to all the questions asked by the Immigration Officer with simple and clear answers, and ask for clarification if they do not understand the question clearly.
Navigating the Airport
Many airports have arrival guides on their websites. We highly recommend students research the airport they will be landing in to get themselves familiar. The 10 most frequently accessed airports in the US are:
- Atlanta Airport (Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport – ATL)
- Los Angeles Airport ( Los Angeles International Airport – LAX)
- Chicago Airport (O-Hare International Airport – ORD)
- Dallas Airport (Dallas Fort Worth International Airport – DFW)
- Denver Airport (Denver International Airport – DEN)
- New York Airport (John F. Kennedy International Airport – JFK)
- San Francisco Airport (San Francisco International Airport – SFO)
- Seattle Airport (Seattle-Tacoma International Airport – SEA)
- Las Vegas Airport (McCarran International Airport – LAS)
- Orlando Airport (Orlando International Airport – MCO)







